By Dhananath Fernando
Originally appeared on the Morning
The Value Added Tax (VAT) increase from 15% to 18% and the removal of about 95 items from the VAT exempted list to a VAT applicable list has raised concern among politicians and people alike.
When taxes change too often, public confusion and erosion of tax revenue both have to be expected. VAT was once 8% in Sri Lanka and then revised to 12%. It was again increased to 15% and finally now to 18%. The VAT threshold was once at Rs. 12 million and later increased to Rs. 300 million. Currently it is at Rs. 80 million and expected to be reduced to Rs. 60 million.
When the VAT threshold was increased to Rs. 300 million from Rs. 12 million, the number of individuals registered for VAT dropped to 8,000 from 28,000. Our policymakers are discussing expanding the tax base after diluting our tax base through our own inconsistent policies.
One of the key principles of taxation is stability, according to the Tax Foundation. The other principles are simplicity, transparency, and neutrality. When tax rates and thresholds are changed often, thIMFe markets and individuals react and tax revenue will erode.
A complicated context
Sri Lanka’s context is sadly more complicated than many other cases. We have given a commitment to the International Monetary Fund (IMF) on increasing our tax revenue because our interest costs are extremely high. Most of the interest is inherited due to bad financial management over the years and there is very little meaning in blaming each other.
On one hand, the Government has no other option but to increase revenue through taxation. However, on the other hand, when taxes are increased the economy will contract. Growth, which is also a key requirement for us to emerge from the crisis, will be affected due to the lowered purchasing power of the people. When the economy contracts, tax revenue will also start to decline.
Given the perennial weaknesses in our tax administration, the Government has selected the most convenient option of VAT to be increased, since it can be collected easily compared to other taxes. VAT is considered to be better compared to other taxes such as the Nation Building TAX (NBT) or the Social Security Levy (SSL), which are considered to be cascading taxes, where throughout the economic process one tax is applied on top of the other.
This leads to a situation where the effective tax rate becomes very high, but with VAT, tax will only be applicable for the value added throughout the supply chain. Also, high income earners generally contribute a higher VAT in total as VAT is a consumption tax. People with higher incomes tend to consume more, so the more they spend, the more taxes the Government can recoup.
The negative impact of VAT can be witnessed when it is applied to food items. The poorest of society gets adversely impacted, since their percentage of expenditure on food is very high compared to people who fall into higher income brackets.
There will be considerable impact on the overall prices for the common people with the new VAT revisions. The price of petrol and diesel is expected to increase by about Rs. 50-60 (provided the other taxes are not changed and global fuel prices remain the same). LP Gas (12.5 kg cylinder) will increase by about Rs. 500-600.
Prices of solar panels, electronic items, laptops, and mobile phones are expected to rise. This will also have an impact on inflation as well, but we need to keep in mind that inflation is always a monetary phenomenon. With high prices, people may consider cheaper alternatives and supply and demand will readjust, provided we keep our monetary policy right.
Solutions
A key solution to bringing down prices of food items is to remove the Special Commodity Levy (SCL) applied to these items. The SCL not only increases prices, but the provisions provided to the minister to impose and remove the SCL overnight opens significant room for corruption. The recent increase of the SCL on sugar to Rs. 50 from 25 cents is a good example of how an overnight gazette creates room for corruption and passes the burden to the people.
Other taxes on food items including CESS, Ports and Airport Development Levy (PAL), and many other para-tariffs should be removed. There is a myth that productivity can be improved by imposing tariffs on domestic food items. If that is the case, our industries for milk, yoghurt, cheese, and many other food items have to be extremely productive and efficient. Instead of domestic product growth, we see the same producers ask the Government for further protection.
Tax competitiveness as a framework
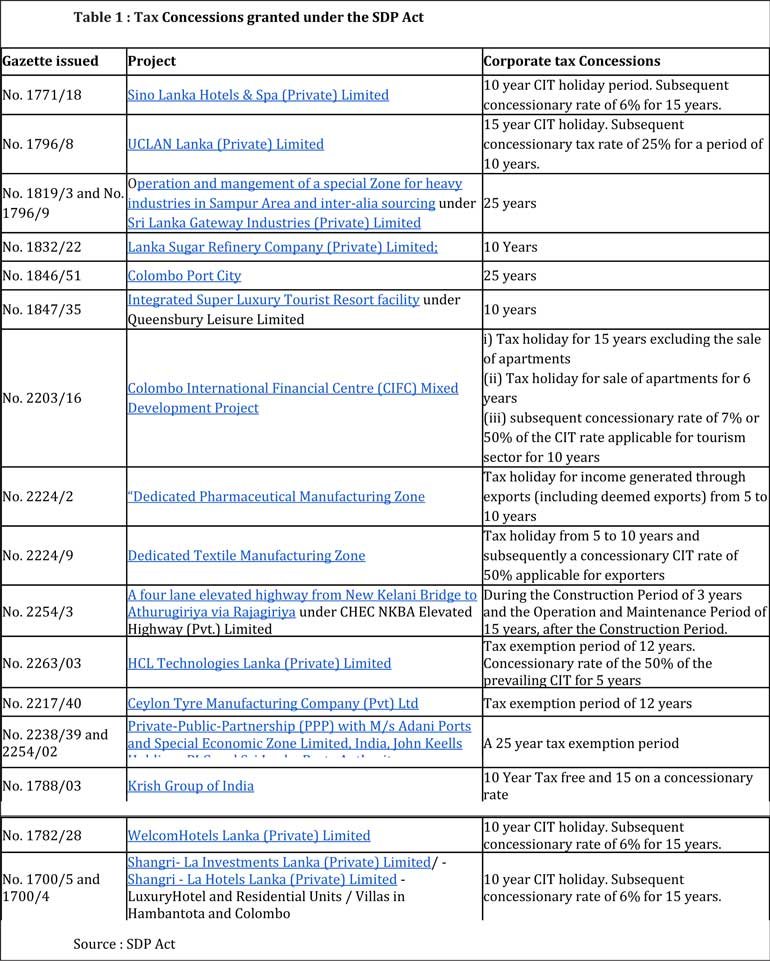
Moving forward, Sri Lanka has to look at tax competitiveness as a framework for thinking about taxes. In the global context, everything is about competitiveness, including the tax system. As an example, if corporate tax is 25% in competing markets in the region, we cannot increase the corporate tax to 30%, only considering the revenue requirement of the Government.
At the same time, we cannot compromise our healthcare and education systems, which help to develop better skills through taxpayer money, by bringing taxes unnecessarily down and compromising our tax revenue. In a market system, competition and prices play a key role, and the same is applicable for taxes, FDIs, and many other variables.
We have to first take the basic steps of improving tax administration. We then have to rationalise our expenditure and spend where we need to spend, thereafter raising revenue by being competitive. A VAT increase to increase Government revenue alone will not solve our macro instability. We have to ensure macro stability by being competitive in all aspects of the economy.