By Dhananath Fernando
Originally appeared on the Morning
The year 2024 will be an election year. The general flow of events is that each political party and candidate will launch a manifesto of a grand-scale and present their plans for the people and the country. Most of these promises will not be implemented or will only be half implemented. In certain cases, the opposite of what was promised will be implemented.
Most manifestos are presented in general terms with a target of 20 years ahead with little data. Many manifestos across all party lines are wish lists with no action plans.
In my view, this time there is a slight difference.
Regardless of the party formation or whoever the presidential candidate will be, there are few reforms that are non-negotiable. Ideally, across all manifestos, there are five basic ideas which have to be the common denominator.
Strengthening social safety nets
Following the worst economic crisis in Sri Lanka’s history and high inflation, about four million people have fallen below the poverty line. That puts seven million people under poverty. The recent Household Income and Expenditure Survey carried out by LIRNEasia and the World Bank indicates significant poverty levels and aftereffects of poverty due to the economic crisis. As a conscientious society, we need to take care of our poor people with the social safety net.
The social safety net is not just an allowance. It is a system and a process of targeting the right people, providing an exit route, and with proper administration. The current Aswesuma programme is making some progress with World Bank assistance, but regardless of the political leader who comes to power, it is a non-negotiable condition that social safety nets have to be strengthened and improved.
The current process has too many loopholes which have to be addressed and improved. Simplifying the process, providing the exit route, and monitoring and depoliticising has to be a continuous effort from the new leadership of the country.
SOE reforms
Thus far, mandatory SOE reforms have been painfully slow. Many parties with vested interests are trying to delay it until the election. However, the continuation of SOE reforms is a must.
Colossal losses, interference in the private sector, intervening in markets, creating an unfair playing field, and inefficiencies are a few reasons why SOEs played a pivotal role in Sri Lanka’s economic crisis. SOEs are vehicles of corruption and have diluted entrepreneurship and Foreign Direct Investments significantly. Without reforming SOEs, the future of Sri Lanka appears to be bleak.
The principles announced by the SOE Restructuring Unit are in the right direction, but the SOE Act and reforms of the Ceylon Electricity Board, Ceylon Petroleum Corporation, and many other networking industries are a must.
Anti-corruption and governance reforms
Execution of anti-corruption laws and governance reforms is another area which has no room for negotiation. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) Governance Diagnostic and many other locally-developed reports on governance provide direction on what needs to be done.
Strengthening our Judiciary system, transparency and accountability in our tax system, removing tax exemptions, and repealing the Special Commodity Levy and the Strategic Development Act too falls under governance and anti-corruption reforms, as those acts provide the legal opportunity for corruption.
There is a strong sentiment from people on the contribution of corruption to the crisis, so taking long-term measures regarding corruption is a must. Anti-corruption and governance reforms go beyond going after corrupt politicians. Rather, it is a system and framework for minimising government influence. Some reforms are complementary and reforming SOEs is also a key component of anti-corruption and governance reforms, as these SOEs play a vital role in corruption.
Following the IMF programme and debt restructuring
Given the international financial architecture, we have no option other than sticking to the IMF programme. We can negotiate some of the actions that we have promised, but overall indicative targets and reforms have to be maintained. Otherwise, it will be yet another incomplete IMF programme and the debt restructuring process will be in jeopardy.
Debt restructuring and the continuation of the IMF programme are very much interconnected. At the moment, external stakeholders are concerned about political instability and in fact, the IMF’s first review identifies the political risks for the continuation of the IMF programme. A commitment from any political leader on sticking to the programme will help Sri Lanka in rebuilding relationships with the world.
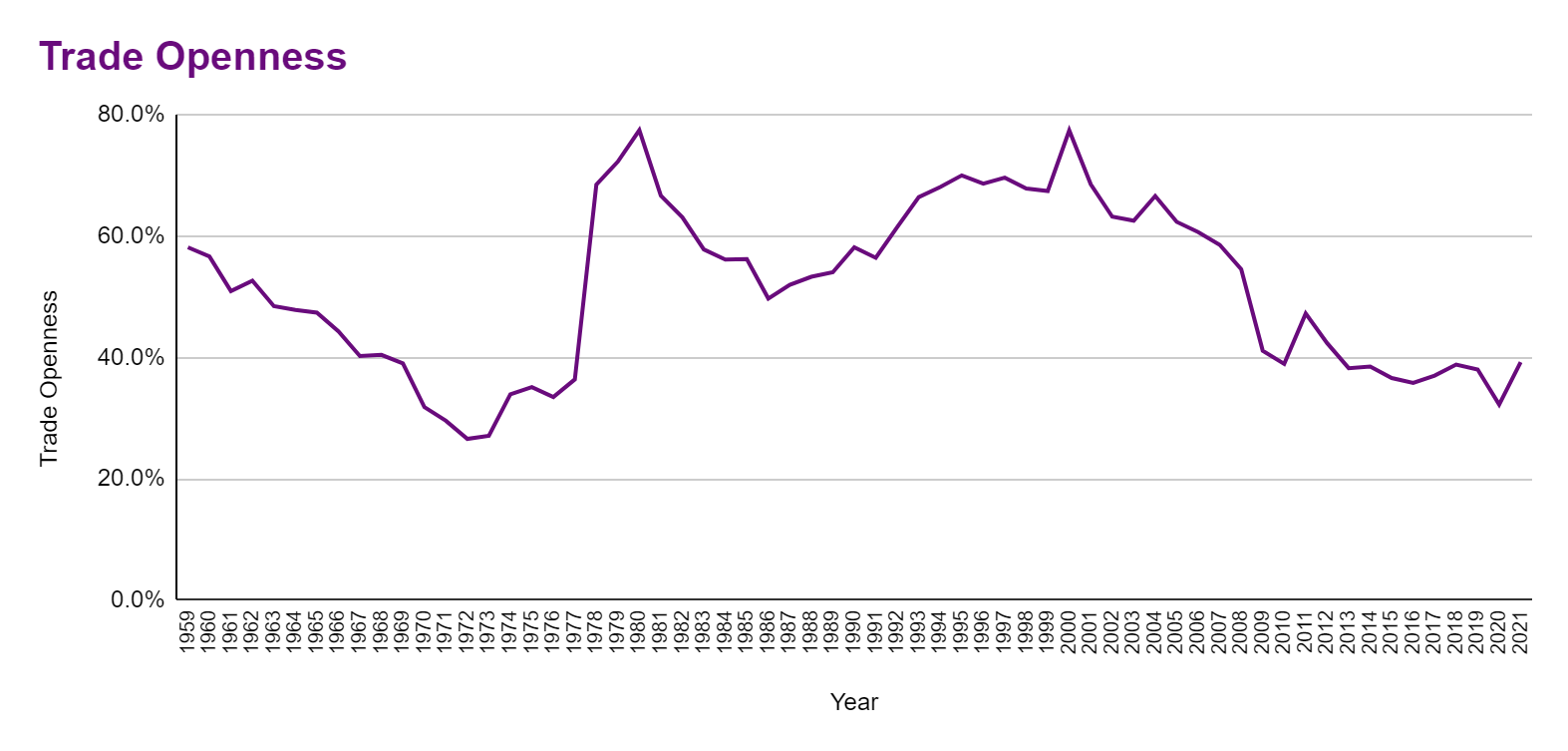
Trade reforms and joining global supply chains
We have to grow our economy to emerge from this crisis. Tax revisions make it likely that growth will slow down and the only solution to grow small island nations like Sri Lanka is through global trade. Our problems regarding global trade are mainly the problems in our own regulations and systems.
We have to remove our para-tariffs and simplify the tariff structure for a few tariff lines. Not only will this help trade, but consumers will also have a greater choice of goods and services as well as competitive prices.
On the other hand, the Government can improve the revenue from Customs since at the moment, the high tariffs are a main reason for revenue leakage in the form of corruption. Trade reforms are about growth, minimising corruption, encouraging exports, and assuring reasonable prices. Even at present, after very high taxes, there are levies such as the Special Commodity Levy, Ports and Airports Development Levy, and a huge array of taxes which hinder the competitive nature of our economy.
These five policies, in my view, are non-negotiable. If any administration deviates from them, it is very likely that we will fall back a few miles behind where we started.