Originally appeared on The Morning
By Dhananath Fernando
Securing the second tranche from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an important step, especially to support our ability to successfully carry out the debt restructuring process. It is not just about the $ 330 million that this tranche brings; it is about the credibility it gives to the reform process and the confidence it instils in the international community, including bilateral and multilateral creditors.
The moment we deviate from the IMF programme and allow our debt to remain unsustainable, we risk regressing to square one. However, we should not get our aims and priorities mixed up. Our aim is not to secure IMF tranches. We need to prioritise achieving deep and meaningful reforms. The IMF tranche will follow as a result.
Ultimately, our goal should be to ensure that, in the future, we never find ourselves in a position where we need to turn to the IMF for assistance.
As this column has discussed many times, it is essential to recognise that the IMF can only stabilise the economy and facilitate credit access, which is a crucial element in our debt restructuring process. The responsibility to clear out the roadblocks that stand in the way of economic growth rests solely on our shoulders. We have to carry out reforms that go beyond the scope of the IMF programme.
Three key reforms aiming to boost economic growth will be discussed below.
Reforms to attract more tourists
Focusing on tourism can significantly contribute to the country’s economic recovery. In addition to bringing in foreign exchange, their spending in domestic markets contributes significantly to Government revenue through VAT. Instead of fixating on the number of inbound tourists, our focus should be on the number of nights a tourist stays in the hotel/country. Simplifying the entry process will attract more tourists, and more importantly, entice them to prolong their stay.
In line with Daniel Alphonsus’ recent article, making the visa process more flexible for tourists is crucial. Our focus should not be on visa fees, but rather to encourage tourists to spend more. This allows local industries to capture the revenue and enhances Government revenue through VAT and various other forms of fees and indirect taxes.
Offering a two-year multiple-entry visa for citizens from countries with a per capita GDP four times higher than Sri Lanka’s is a strategic move to attract high-income tourists. Given our current fiscal situation, carrying out extensive global promotional campaigns are beyond our financial capacity. Therefore, our focus should shift to initiatives that can be implemented effectively with just a stroke of a pen.
Addressing labour force shortages
Retaining skilled talent within Sri Lanka is a challenge faced by many industries, including blue chip companies. These labour shortages are anticipated to affect us from next year onwards, jeopardising the sustainability of existing businesses.
To address this issue and prevent businesses from relocating, it is essential to allow companies the flexibility to recruit from international markets. This approach is crucial to sustaining businesses and their supply chains. Permitting companies to hire skilled labour from outside Sri Lanka will not only alleviate pressure on the country’s labour market, but also offer advantages to consumers and businesses competing in global markets.
Further, it encourages the transfer of knowledge and skills, leading to improved productivity. For example, collaborating with professionals from countries like Japan could introduce advanced productivity management techniques, enhancing overall efficiency. Free movement of people is a crucial step in improving our productivity and driving the economic growth of the country.
If relaxing labour market regulations proves too complicated, a pragmatic alternative is to permit foreign spouses of Sri Lankans to work in Sri Lanka. This measure could help in attracting more skilled workers, providing an incentive for Sri Lankans with families of mixed citizenship to return and settle here. Importantly, this reform won’t incur any costs for the Government; it simply involves changing existing regulations.
Industrial zones for private sector and simplifying tariffs
For us to emerge from this crisis, our primary focus should be on global trade. The complicated tariff structure that is currently in place enables corruption and is a source of frustration for both exporters and importers. Simplifying the tariff structure into three to four tariff bands is essential to streamlining Government revenue administration.
The existing high and complicated tariffs lead to massive leakages of tariff revenue. Moreover, these tariffs discourage imports, hampering productivity and burdening consumers. Implementing a straightforward tariff structure is imperative, removing para-tariffs such as CESS and PAL. Furthermore, we must ensure that the tariff structure for any HS Code is easy to compute and has minimal deviations.
A significant bottleneck in our system that hinders investments and export growth is the shortage of land for industrial activities. Currently, 95% of the land in Board of Investment (BOI) industrial zones in the Western Province is occupied. Investors are required to obtain approximately 17 approvals in order to set up operations and this process can take more than two years.
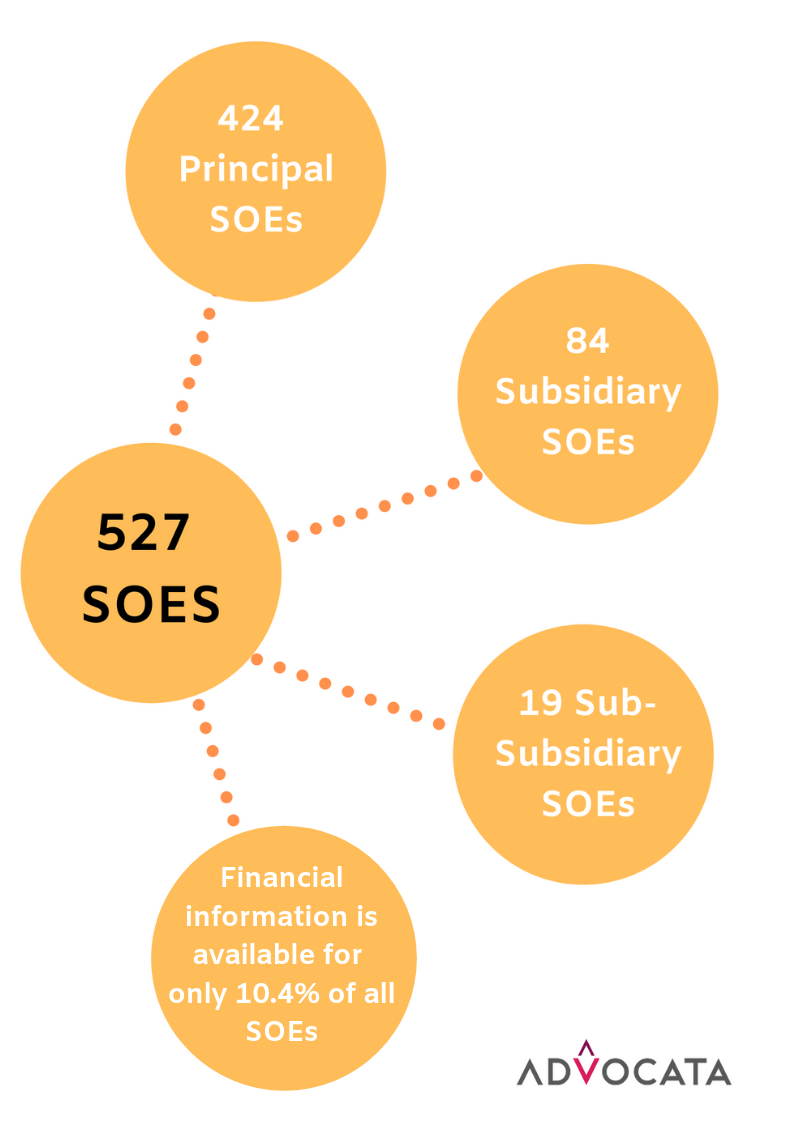
Regrettably, the BOI has not initiated any development projects in the last 15 years. A viable solution that the Government should consider is utilising State-Owned Enterprise (SOE)-owned land and allowing the private sector to develop industrial zones on it.
Private sector-run industrial zones can operate as a plug-and-play model, where the private sector attracts investors and secures the necessary approvals in advance. This approach does not require any Government investments; in fact, it can generate more revenue for the Government through leasing or selling the land for development.
If Sri Lanka is genuinely committed to economic growth and recovery from the crisis, our primary focus should be on implementing these reforms rather than solely relying on the IMF. While the IMF can provide us with short-term stability, it’s our responsibility as Sri Lankan citizens to shape our own growth narrative.