In this weekly column on The Sunday Morning Business titled “The Coordination Problem”, the scholars and fellows associated with Advocata attempt to explore issues around economics, public policy, the institutions that govern them and their impact on our lives and society.
Originally appeared on The Morning
By Dilshani N Ranawaka
Rukshani, is a small business owner running her own grocery store. Her peak hours of business are when everyone gets back home from their jobs around 7-8pm after working in Colombo. Unfortunately, she has been struggling to make ends meet as of late, due to power cuts that are also scheduled in her area around the same time as her peak hours. With just candles lit during these hours, refrigerators and coolers switched off, it adds an additional cost for her to operate her business.
Thilina, who works in Colombo faces a challenge of getting back home as the workers of the Railway Authority have decided to go on strike asking for a pay raise. Even though trains are over-crowded, they are unfortunately the fastest way of commuting back and forth. Alternatively, Thilina has to resort to the next best solution in his capacity; buses, which incurs an additional cost to reach home.
How is that Rukshani and Thilina have no say over the situation? Why does Rukshani have to suffer losses during the peak hours of her business and why should Thilina have to look for alternative transportation for something they are capable of paying, but somehow is beyond their control?
Trains and electricity are two vital services for the day to day functioning of the country. Why do these authorities continue to function when they are failing to provide reliable and efficient services to their customers who pay for these services? They have a monopoly over this service, hence they exploit it.
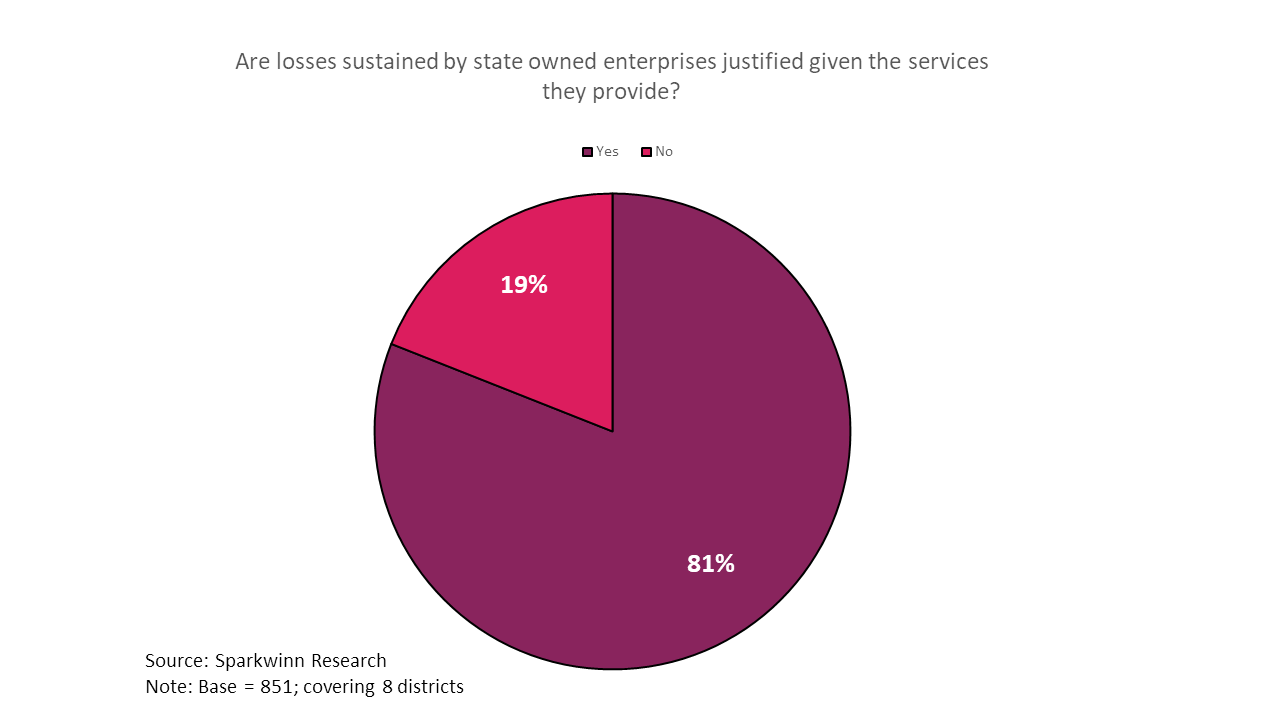
As of 2017, Sri Lanka Railway (SLR) sums up for Rs. 7.5 billion in losses. The Central Electricity Board (CEB) projects of Rs. 89 billion in losses for 2019. An island-wide poll by Sparkwinn Research, commissioned by Advocata Institute indicates that 81% of the sampled population are not satisfied with the performance of the State Owned Enterprises (SOEs). As the numbers have spoken, people are clearly not in favour of having these underperforming SOEs.
Would a private institute still run under these terrible, burdening losses?
The issue mainly starts with the monopolistic control over services complemented with organized trade unions within these public institutions. The fact that these services do not have competition, offers a fundamental background for wage increases and other demands that usually result in strikes which influences the entire population.
The initiation of these services dates back to the years when the private sector had inadequate resources to facilitate these services. In such conditions, the government established these entities for the benefit of the population. However, due to the monopolistic nature of these establishments, workers were able to unionize forcing the government to lose control over these institutions.
To add on to the burden of failures, is the fact that all these are controlled and heavily subsidized by the government. The lack of incentives to improve their efficiency and productivity are therefore felt heavily by the government.
There are common practices of addressing the issues on monopolies of the economy. Incentivizing merger policies, regulating and controlling the quality of these monopolies and price caps are some of the methods developed countries use to provide better services.
The “P” word; “privatization” is a taboo in Sri Lanka, although it is commonly agreed that the process of privatization paves the way towards an answer to address these issues that burden the entire economy.
“Privatization” in Sri Lanka is identified as “transferring an institute from public ownership towards private ownership”. This is only one such form of privatisation and is known as a “complete privatization”. However, there exists various forms of privatizations such as transferring assets, Public-Private Partnerships and franchising.
Path towards privatization
The process of privatization should be methodological. Montreal Review (an independent online magazine) identifies few principals that would lead to an efficient privatization process.
The purpose of privatisation
The need to review different methods of privatisation
The extent of the privatisation
Recognising constraints
Finding a buyer
Implementing an investor friendly environment to attract investors
How the United Kingdom excelled in their privatization process of trains and telecom are case studies which could be replicated in Sri Lanka. The United States government remained in control of quality control and maintaining standards while the operations were handled by private sectors. On the other hand, the United States had successfully privatised industries with natural monopolies such as water and electricity supply by the privatization of operations with the government remaining in control of providing the role of maintaining standards while removing excess burden on the budgets.
However, given the extensive amount of State Owned Enterprises (SOEs), an initial step towards privatization could be to list down possible institutions or even better, towards creating an index which could be a measurement towards qualifying for privatization process.
Can we breakdown these natural monopolies? Are monopolies simply an excuse that gives the governors the luxury of political lobbying? Something to think about.
“The very term “public consumption products” is an absurd one. Every good is useful “to the public”, and almost every good may be considered “necessary”. Any designation of a few industries as “public utilities or services” is completely arbitrary and unjustified” - Murray Rothbard, a prestigious American Economist.