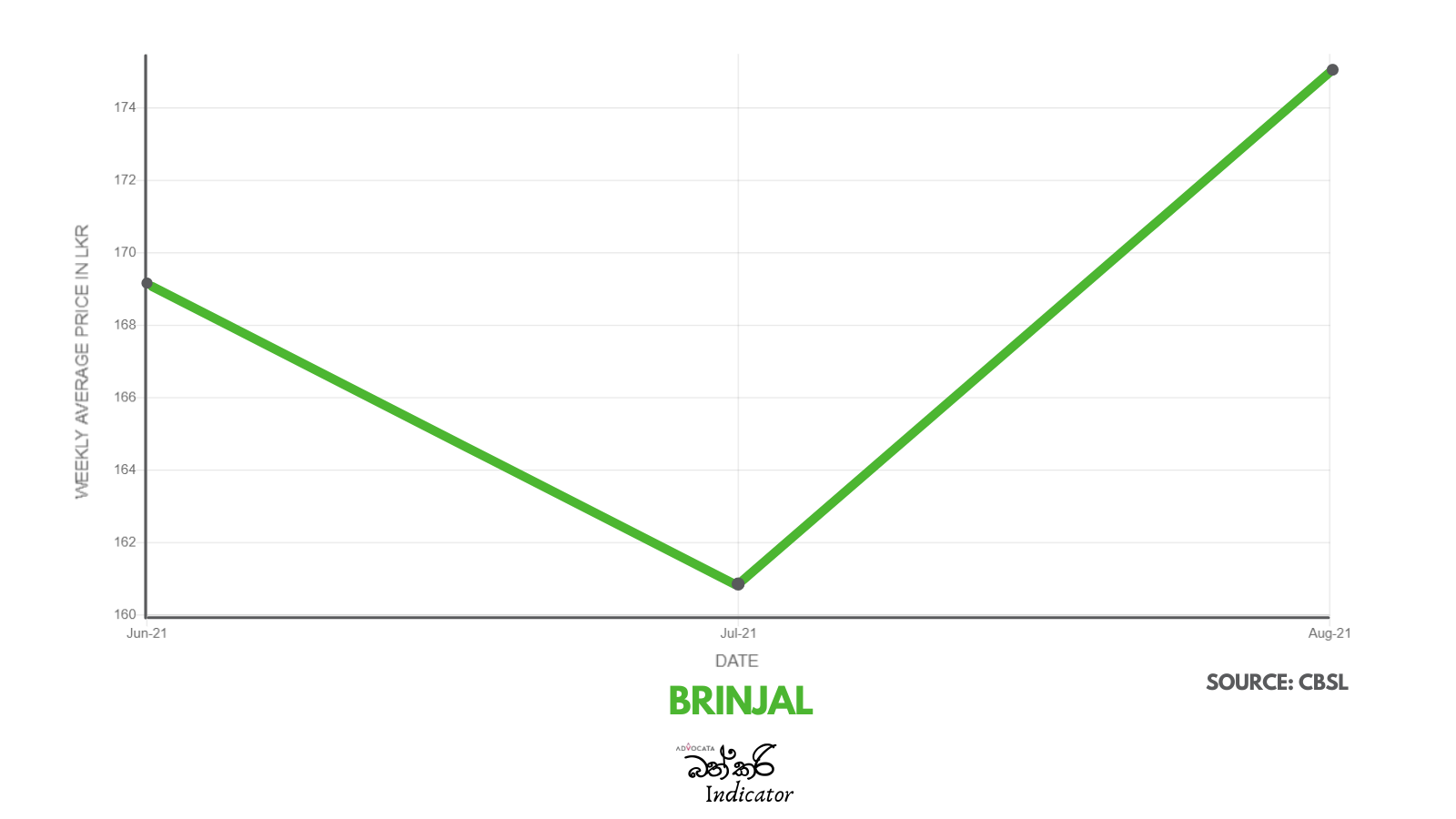
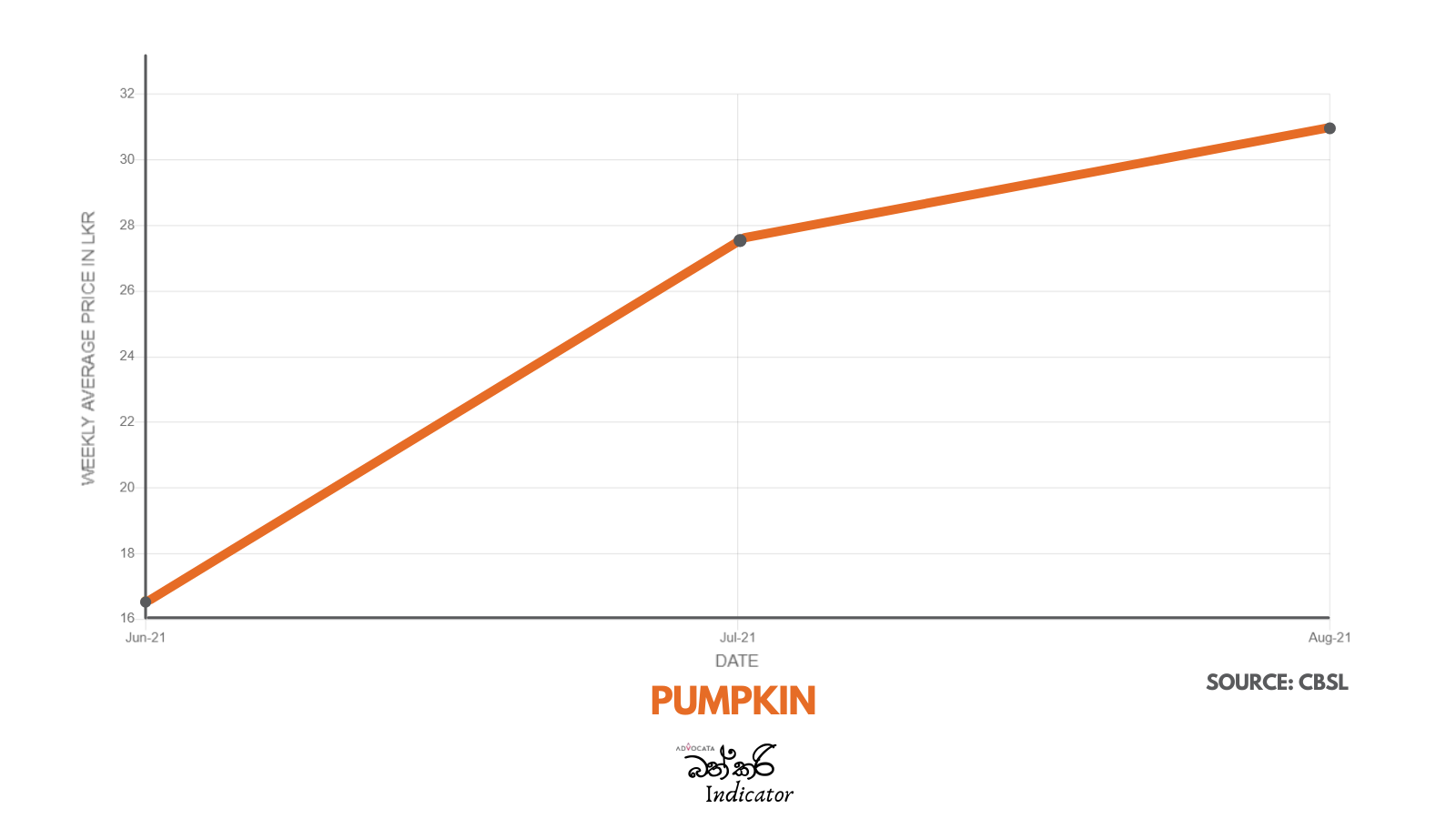
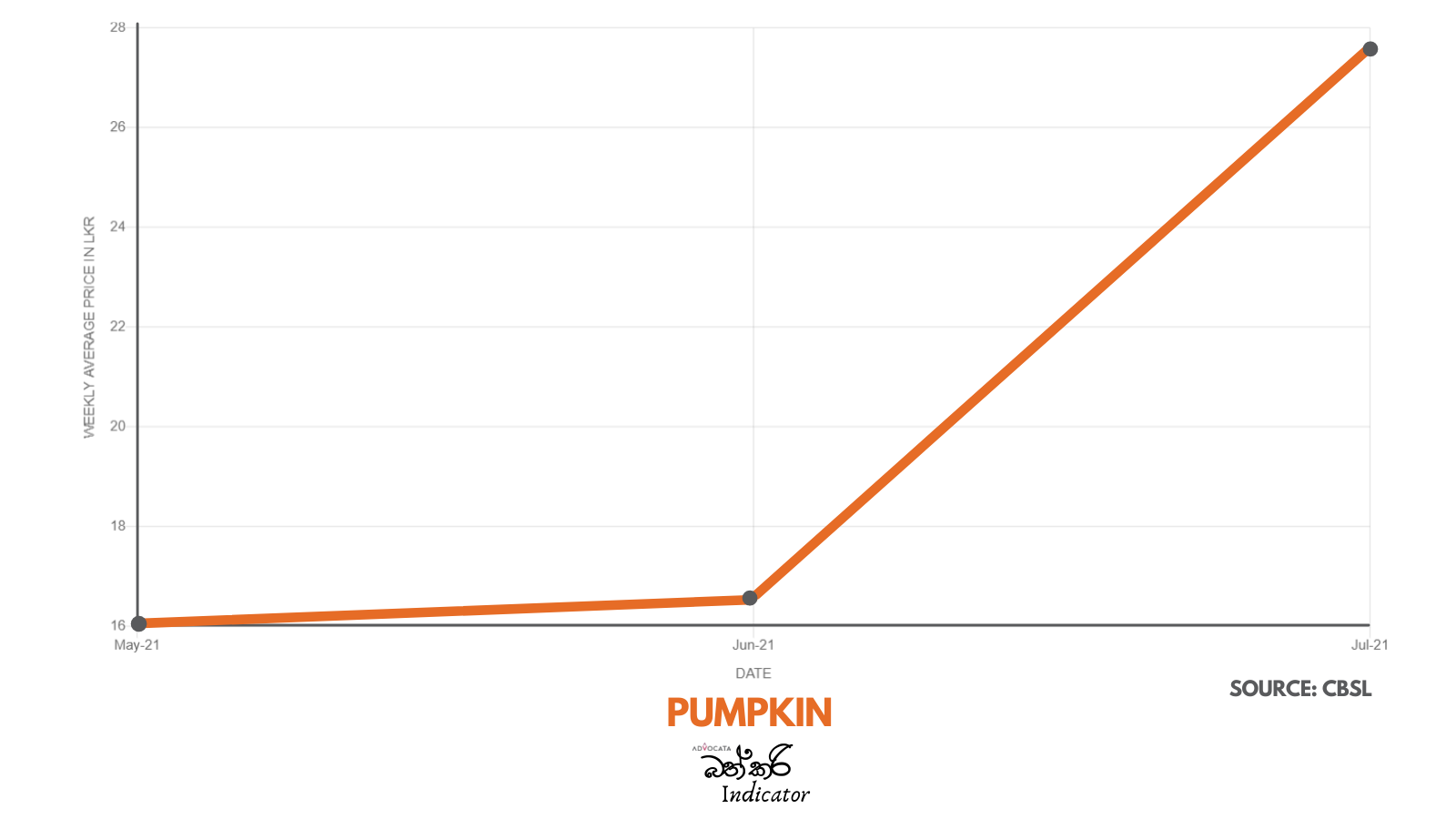
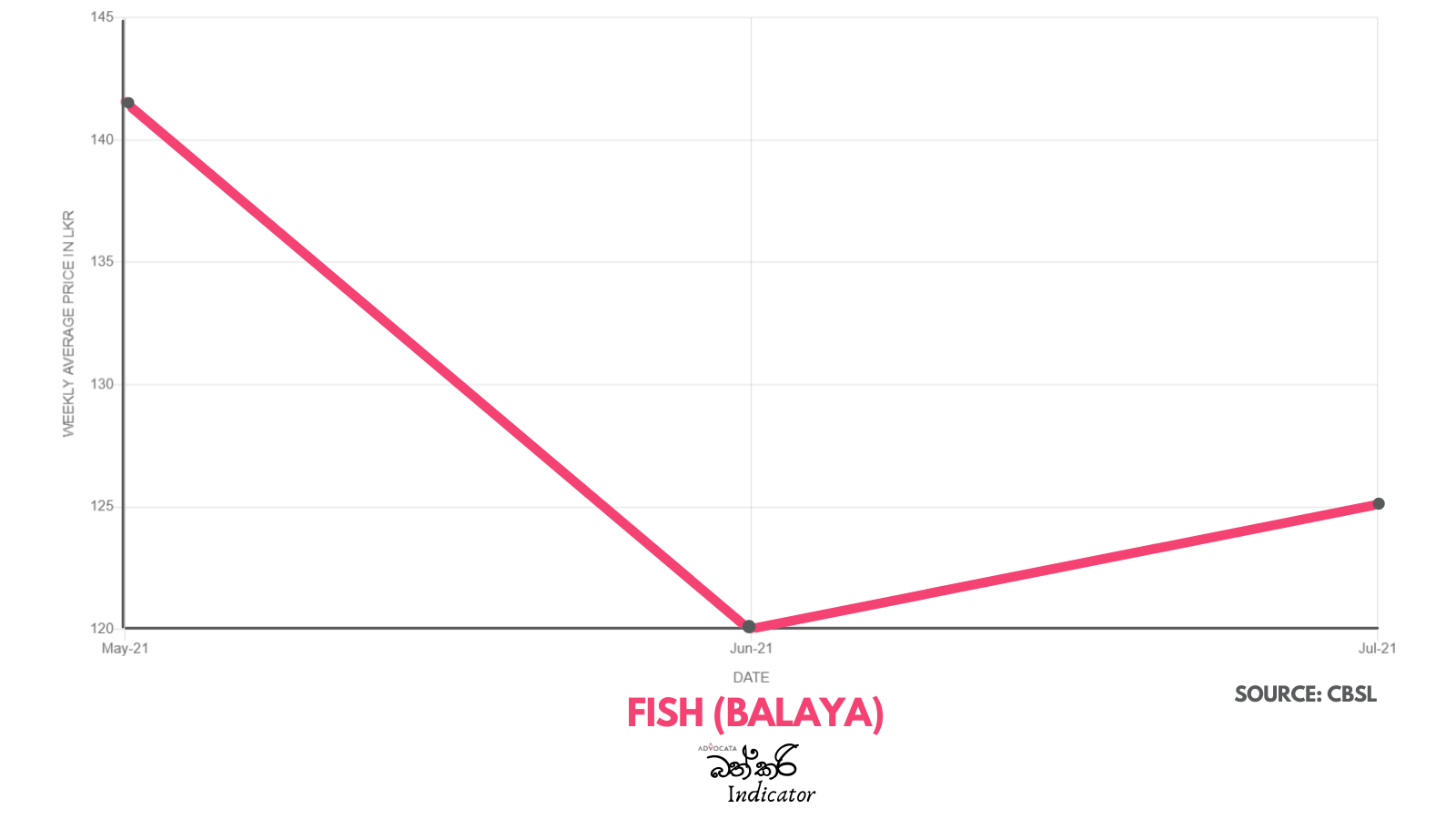
GSP Plus vital for SL to fight competition – EU Ambassador
After 2010 Sri Lanka’s exports to the European Union (EU) have increased by 60% but half of it is through the Generalised Scheme of Preferences (GSP) plus, stated EU Ambassador to Sri Lanka Denis Chaibi, speaking at a virtual conference organised by Colombo-based think-tank Advocata Institute.
Vietnam increased by 400% and Bangladesh by 150% during the period from 2010 to 2019, thus to stay ahead of competition, GSP plus is significant for Sri Lanka, stated Chaibi. Ambassador further noted that retaining GSP Plus would give a positive image for Sri Lanka that it is committed to human rights obligations. “The EU market is competitive as it is a superpower in terms of product quality standards.
For a Sri Lankan exporter to export to the EU would give the exporter recognition in any other market as the EU only accepts products with certain standards. Sri Lanka is already in a forex crisis. Increasing exports is a way out of the current crises. COVID-19 has created a resilient supply chain but without preferential access it is difficult for Sri Lanka to increase its exports to EU markets.
Read the full article here
SL’s economic recovery led by trade
The Covid-19 pandemic has revealed the real weaknesses Sri Lanka had in terms of its economy for the past four decades.
With the foreign exchange shortage worsening day by day, many fear that the country will go back to the pre-1977 era of ration cards to purchase essential food items, as the importation of such goods will be impossible in the near months.
Sri Lanka needs economic reforms that will decide the fate of the country in the next few decades to come, and many experts say that reforms should start with the country’s protectionism trade that has not really evolved over the years.
Productivity for growth
Speaking at a webinar organised by the Advocata institute, its Chair – Academic Programme Dr. Sarath Rajapathirana said that Sri Lanka has failed to make any substantial reform for the economy, particularly on trade-side reforms, for the last 20 years.
He said trade is very important as it exposes the country to competition and among other areas such as the fiscal side, the budget, and having a proper monetary policy that avoids inflation and contributes to a more stable exchange rate, trade too needs a lot of work.
“Our imports are three times the value of exports, so we have been continuing a trade deficit, which is also accompanied by a current account deficit. These have to be addressed when talking about trade reform; we have to have the macroeconomic support for it,” he said.
He said more than the aggregates of imports and exports, the encouragement to productivity from having open trade or non-restricted trade is more important.
“If you don’t have strong growth in productivity, we have to keep on increasing the factors of production. It is difficult because we need to have more savings and less consumption. So the best way to get it done is to really have a system in which our reforms are going to immediately affect the positive side of our productivity growth,” he noted.
Read the full article here
Increased int’l trade participation key to achieving economic recovery, says top economist
As the national economy continues to face new challenges from multiple angles and their implications are being very much felt by businesses and masses, Dr. Rajapatirana called for the government to start by having in place a more streamlined tariff structure.
“First get rid of para tariffs fast. And then look to introduce a single uniform tariff,” asserted Dr. Rajapatirana while addressing a webinar hosted by the Advocata Institute, this week.
For Sri Lanka to embark on any efforts that would assist in the recovery of the national economy, Dr. Rajapatirana stressed it is essential for the relevant authorities to acknowledge the importance of international trade when charting the path for progress.
He pointed out that Sri Lanka needs to get away from its protectionist mindset and the way to get about it is to first look at lowering the existing tariff.
“The existing para tariff hurts our competitiveness. This is one of the fundamental things we need to do,” said Dr. Rajapatirana.
He added that the government must also explore the option of introducing a uniform tariff of about 15 percent, which can be reduced over a period of time.
Dr. Rajapatirana opined that by bringing about the suggested changes, Sri Lanka would be signalling to the world that it is serious in wanting to achieve economic progress.
Dr. Rajapatirana also pointed out that the country has not made any substantial economic reforms, especially on the trade side, in the last 20 years or so.
As the country continues to grapple with the COVID-19 pandemic along with the rest of the world, Dr. Rajapatirana warned that neglecting the economy would only further delay the recovery process.
“We cannot think of economic recovery without really starting trade reforms. We are in a good driving seat to undertake the reforms since the government has two-thirds majority.
We need to have the macrocosmic reforms that come from the monetary policy and the fiscal policy. Without that you don’t have the sort of dynamic stability that is needed to put in place a good reform programme,” he said.
Read the full article
Sri Lanka international trade role in Advocata forum as monetary instability drive import controls
Colombo-based think tank Advocata Institute said it is hosting an online forum on ‘The Role of International Trade in Economic Recovery in Sri Lanka’, as the island is mired in the worst import controls since the 1970s after printing money.
Trade controls started during as money was printed to target an ‘output gap’ involving curbs on gold trading and vehicles and other items, escalated into full-scale import substitution, import bans and tightened from 2020.
Sri Lanka’s post-independent economic history is littered with administrations that tried to operate various economic plans without reforming a soft-pegged central bank with activist monetary policy.
Read the full article